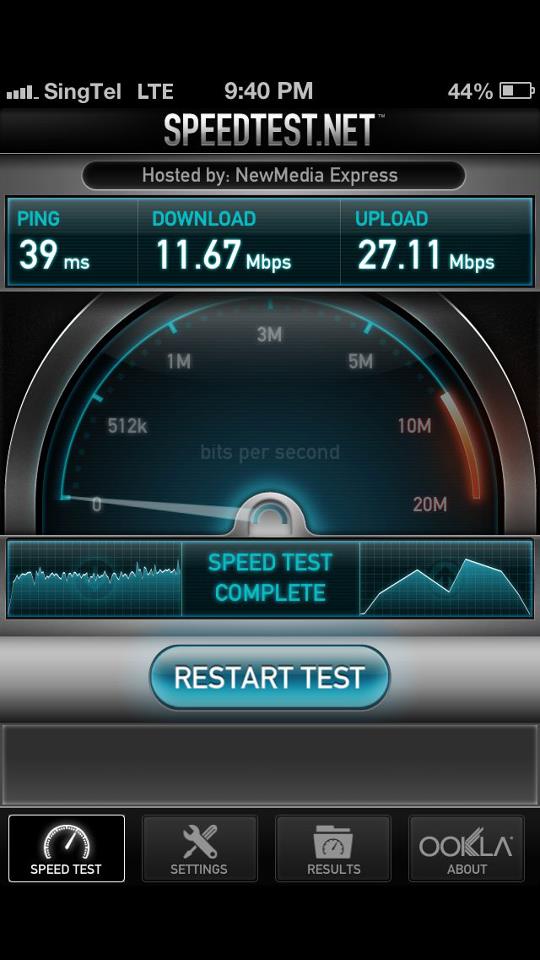
In the modern era where internet speed is paramount, understanding the nuances of speed tests is essential. While these tests offer insights into your connection’s performance, misconceptions abound regarding their accuracy. Here, we delve into common myths surrounding speed tests and provide actionable tips for obtaining more reliable results.
Factors affecting benchmark results

Server Location: The distance between your location and the server you select for testing is a critical factor. Opting for a server closer to your vicinity typically yields more accurate results due to reduced latency and network congestion. However, this alone doesn’t guarantee precision. Some ISPs or telcos may prioritize or throttle speeds to specific servers, distorting the results. Notably, testing on neighboring country servers has shown significant speed improvements due to the absence of throttling.
Network Congestion: Time of day and local internet usage heavily influence speed test results. Peak hours often result in slower speeds due to heightened network congestion. Factors such as shared network infrastructure and ISP bandwidth allocation play a significant role in determining test outcomes.
Type of Server: Each server has allocated bandwidth for public tests, with some capped at 1 Gbps and others at 10 Gbps. If you’re aiming to test a fiber broadband connection, it’s advisable to select a server capable of accepting higher bandwidth to ensure accurate results.
Local Network Conditions: Issues within your local network, such as Wi-Fi interference or outdated hardware, can affect speed test results. Poor signal strength or network congestion can contribute to suboptimal performance.
Hardware and Software Factors: The performance of your device, including hardware specifications and software configuration, influences speed test results. Factors such as processing power, browser efficiency, and background applications consuming bandwidth can impact accuracy.
Wired vs. Wireless Testing: It is more accurate to use a wired connection for speed tests instead of wireless. Wireless connections can hamper speed due to interference or using older devices with newer routers, leading to inaccurate results.
How to Get More Accurate Speed Test Results: To ensure precision, choose a less congested, non-throttled server, locally or abroad. Conducting multiple tests at different times provides consistency and a broader understanding of performance. You can also choose to use other speedtest applications and do a comparison. Alternatively, setting up your own speed test scripts allows complete control over the testing environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while speed tests are valuable tools for evaluating internet connection performance, it’s essential to understand the factors that influence accuracy. By considering these factors and implementing best practices, you can obtain more reliable results tailored to your specific needs.