NB-IoT the most efficient way to power devices for a smart city
bluetooth 9 Aug 2017
Yesterday, M1 Ltd showcased some of it’s partner’s products at it’s launch of NB-IoT network in Singapore. So, what is IoT and how does it form the basis for forming a smart nation ?
First of all, we must understand what is NB-IoT. NB-IoT stands for Narrow Band – Internet of Things.
Currently, in any outdoor environment, be it flood monitoring, Air quality monitoring, data are being sent via the traditional 3G/4G dongle/data SIM. While this works, it takes up bandwidth and the device requires a SIM card that does nothing but more than just sending periodic data back to the server end for processing. Smartphone users will know how battery hungry these radios are. They probably last you last than one day. So, the challenge of NB-IoT is to reduce battery usage and the reception must be available 99.99% in terms of coverage.
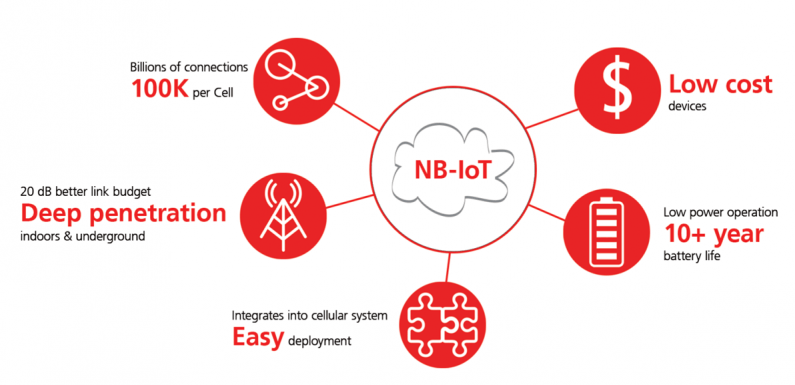
So, there we have Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT), a standards-based low power wide area (LPWA) technology developed to enable a wide range of new IoT devices and services. NB-IoT reduces power consumption and has deep and wide coverage. Battery life of more than 10 years can be supported for a wide range of use cases.
It is simpler than current GSM/GPRS design and resides within the guard band of LTE bands. Current design uses the 900MHz band with implementations using AT command. If you are familiar with modems, AT command set shouldn’t be new to you to design a system to poll results from a device over the IoT network. The transfer bit rate is only 512kbps which is really low.
To cater to the ever increasing number of IoT devices in future, the implementation uses IPv6 address. NB-IoT can co-exist with 2G, 3G, and 4G mobile networks and supports all the security and privacy features of mobile networks, such as support for user identity confidentiality, entity authentication, confidentiality, data integrity, and mobile equipment identification.